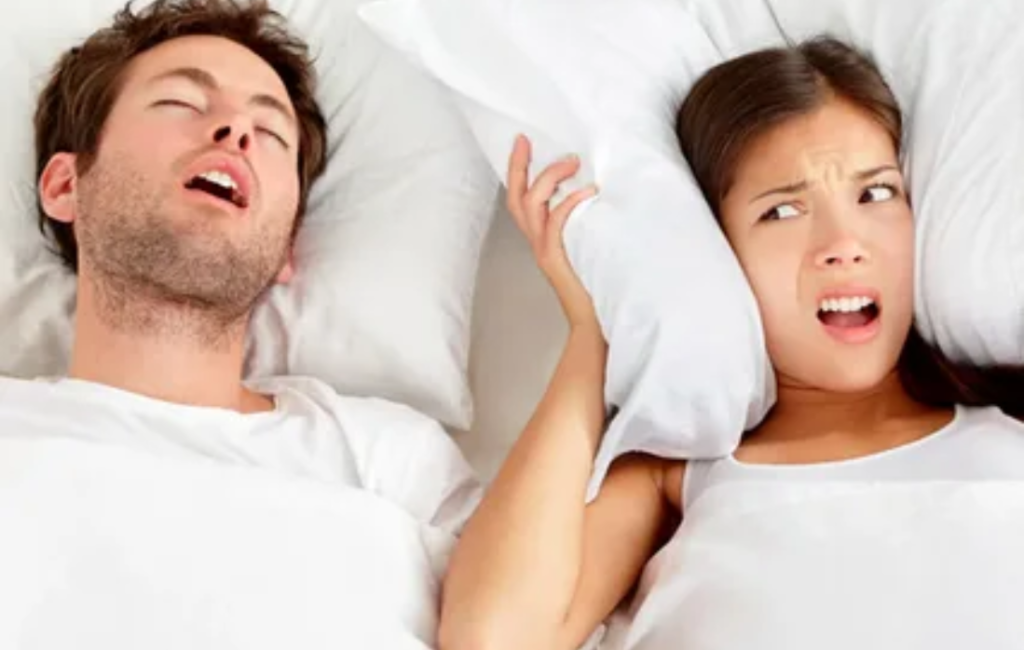
Sleeping is not just about rest; it’s a crucial time for our body to repair and rejuvenate. However, for many people, especially those with Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), sleep can be disrupted by snoring and breathing difficulties. Interestingly, the position you sleep in can significantly influence these issues. Let’s delve into how different sleeping positions affect snoring and OSA, and what you can do to improve your sleep quality.
The Role of Sleeping Positions
- Back Sleeping (Supine Position): Sleeping on your back is a common position but can worsen snoring and OSA. When you lie on your back, gravity pulls the base of your tongue and soft tissues of the throat backward, which can obstruct your airway. This obstruction leads to snoring and, in more severe cases, can cause episodes of apnea where breathing temporarily stops.
- Side Sleeping: Side sleeping, particularly on your left side, is often recommended for those with snoring and OSA. It can help keep your airways open and reduce the likelihood of obstruction. This position may prevent the tongue and throat tissues from collapsing into the airway, thereby reducing snoring and improving breathing.
- Stomach Sleeping (Prone Position): It’s generally advised against sleeping on your stomach because it can put strain on your neck and spine. It may also contribute to snoring and OSA in some individuals because it can restrict breathing by putting pressure on the chest and diaphragm.
Effects of Sleeping Positions on OSA
- Back Sleeping and OSA: Individuals with OSA often experience more frequent and severe episodes of apnea when sleeping on their back due to increased airway collapse.
- Side Sleeping and OSA: Side sleeping can reduce the severity of OSA by keeping the airway more stable and open. This position is especially beneficial for those with mild to moderate OSA.
- Stomach Sleeping and OSA: Sleeping on your stomach may worsen OSA symptoms in some cases, although individual experiences can vary.
Tips for Better Sleep
Improving your sleep posture can positively impact snoring and OSA:
- Use Pillows: Supporting your head and neck with pillows can help maintain a better sleep position, especially if you tend to sleep on your back.
- Sleep Hygiene: Maintain a consistent sleep schedule, avoid caffeine and heavy meals before bedtime, and create a comfortable sleep environment.
- Consultation with a Specialist: If you suspect you have OSA or if your snoring is severe, consult with a sleep specialist. They can conduct sleep studies and recommend treatments such as CPAP therapy or oral appliances.
Summary
Your sleeping position plays a crucial role in managing snoring and OSA. While side sleeping is generally recommended to reduce symptoms, individual preferences and comfort also matter. If you’re experiencing persistent snoring or suspect you have OSA, seek professional medical advice. A sleep specialist like Dr. Yogesh Agrawal, located in Wakad, Pune, at the Best Sleep Apnea Clinic in Pune, can provide personalized guidance and treatment options to help you achieve better sleep and overall health.
Understanding how your sleeping position affects your breathing can lead to more restful nights and improved quality of life. Experiment with different positions and consider professional advice to find what works best for you. Prioritizing good sleep hygiene and seeking appropriate medical care can make a significant difference in managing snoring and OSA effectively.