Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive respiratory condition that significantly impacts breathing. Among its various forms, chronic bronchitis stands out for its persistent cough and excessive mucus production in the bronchial tubes. Smoking plays a pivotal role in exacerbating these symptoms, worsening the quality of life for individuals suffering from this debilitating disease.
Understanding Chronic Bronchitis in COPD
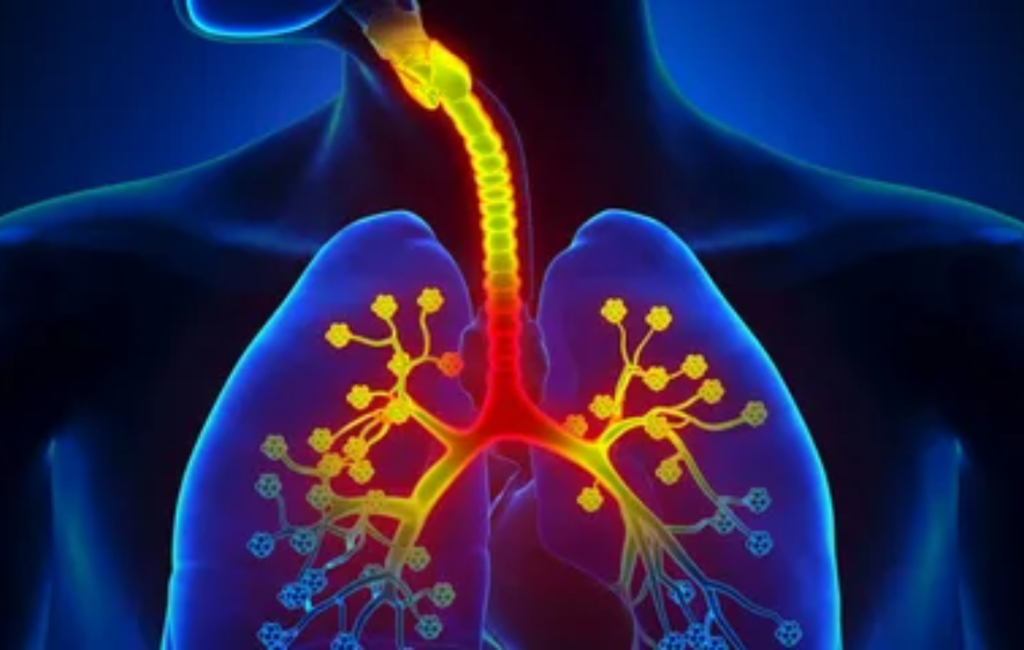
Chronic bronchitis is characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which are responsible for carrying air to and from the lungs. In individuals with COPD, this inflammation becomes chronic and leads to increased production of mucus, narrowing the airways and making breathing difficult. Symptoms include a persistent cough with mucus, wheezing, and shortness of breath, especially during physical exertion.
The Role of Smoking
Smoking is the primary cause of chronic bronchitis in COPD. The chemicals in tobacco smoke irritate the lining of the bronchial tubes, triggering inflammation and swelling. Over time, this chronic irritation leads to the thickening of the bronchial walls and an increase in mucus production. Smoking also impairs the function of cilia, the tiny hair-like structures that normally sweep mucus and debris out of the airways. This further contributes to the accumulation of mucus and debris, obstructing airflow and worsening symptoms.
Impact on Respiratory Function
Smoking exacerbates the progressive nature of COPD by accelerating lung damage. The toxic chemicals in cigarette smoke cause oxidative stress and inflammation in the lungs, which damages the delicate tissues responsible for gas exchange. This damage results in decreased lung function and exacerbates symptoms such as coughing and breathlessness.
Complications and Health Risks
Smoking not only worsens the symptoms of chronic bronchitis but also increases the risk of developing complications such as respiratory infections, pneumonia, and exacerbations of COPD. These exacerbations are episodes where symptoms suddenly worsen, often requiring hospitalization and intensive treatment. Smoking cessation is crucial in managing COPD as it slows the progression of the disease and reduces the frequency and severity of exacerbations.
Secondhand Smoke and Environmental Factors
Exposure to secondhand smoke and other environmental pollutants also contributes to the aggravation of chronic bronchitis symptoms in COPD. Secondhand smoke contains many of the same harmful chemicals as directly inhaled smoke, putting non-smokers at risk of developing respiratory conditions similar to those of active smokers. Minimizing exposure to smoke and pollutants is essential for managing COPD and improving overall respiratory health.
Treatment and Management Strategies
Effective management of chronic bronchitis in COPD involves a combination of medications, pulmonary rehabilitation, and lifestyle modifications. Medications such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids help alleviate symptoms and reduce inflammation in the airways. Pulmonary rehabilitation programs focus on exercise training, nutritional counseling, and breathing techniques to improve lung function and quality of life. Lifestyle modifications include smoking cessation, avoiding respiratory irritants, and maintaining a healthy diet to support respiratory health.
Importance of Smoking Cessation
Quitting smoking is the single most effective intervention in slowing the progression of COPD and reducing the severity of chronic bronchitis symptoms. It is never too late to quit smoking, and even individuals with advanced COPD can benefit from cessation. Quitting smoking decreases inflammation in the airways, improves lung function, reduces the frequency of exacerbations, and enhances overall quality of life. Support from healthcare providers, smoking cessation programs, and counseling services can significantly increase the success rate of quitting smoking.
Summary
Smoking significantly exacerbates the symptoms of chronic bronchitis in COPD by causing chronic inflammation, increased mucus production, and accelerated lung damage. Quitting smoking is crucial in managing COPD effectively and improving respiratory function. For expert guidance and comprehensive care for chronic bronchitis in COPD, visit Dr. Yogesh Agrawal at Thergaon, Pune, recognized as the Best Sleep Specialist Clinic in Pune. Taking proactive steps to quit smoking and adopt a healthy lifestyle can lead to better outcomes and a better quality of life for individuals living with COPD.